Types of eBike Motors: Front Hub, Rear Hub, or Mid-Drive?
The right ebike motor makes all the difference in finding your perfect electric bike. The motor acts as the system’s heart and works with the battery and display to give you the power you need. Two main types exist: hub motors and mid-drive motors. Hub motors stand out for their durability and need little maintenance. They’re also the budget-friendly choice. Mid-drive motors cost more due to their complex design, but many cyclists rate them as mechanically better.
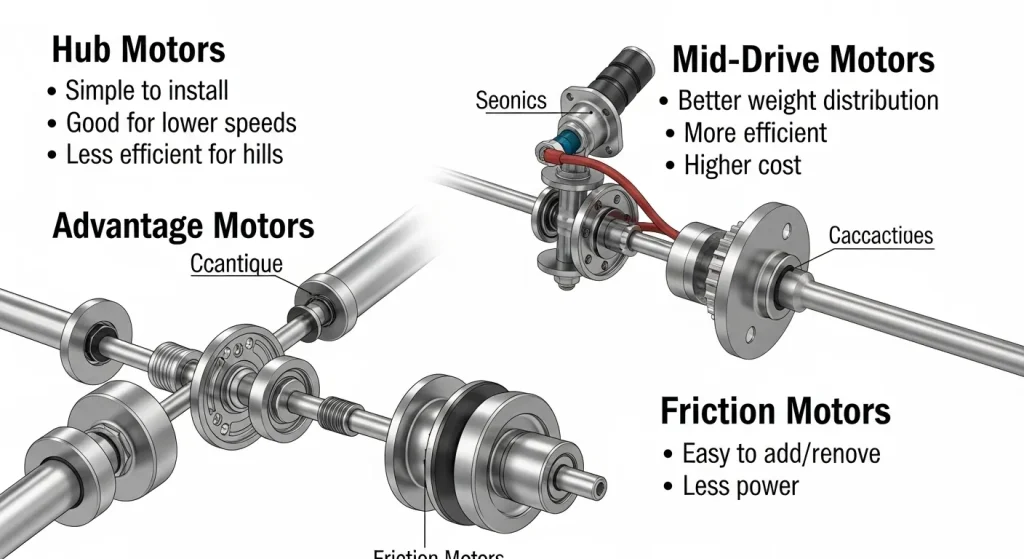
This piece dives into what sets front hub, rear hub, and mid-drive motors apart. You’ll learn how each motor handles different riding situations. Mid-drive motors adapt fast to changing conditions, while rear-hub motors shine on flat or slightly hilly terrain. After reading this, you’ll know the ins and outs of electric bike motors and can pick one that matches your riding style.
How eBike Motors Work and What They Do
Electric bike motors play a crucial role by converting electrical energy into mechanical force. Modern motors use brushless DC technology that eliminates traditional brushes for current alternation. The system relies on three key components: the motor, a controller that acts as the brain, and a power-supplying battery.

Types of Motor Assistance
Riders experience motor assistance in two main ways. The first uses cadence sensors that activate power based on pedaling speed and deliver steady power whatever the effort. The second option uses torque sensors to detect pedaling force and adjust the power output. These sensors can boost your pedaling power up to 300%. The technology’s impressive responsiveness comes from its ability to take 1,000 measurements in each pedal stroke.

The Role of the Controller
The controller works as the heart of the system and processes signals from throttle or pedal assist systems to regulate current flow to the motor. It adapts to changing conditions and maintains peak performance on different terrains.
Motor Power and Torque
Motor power ranges from 250W to 750W, which determines the bike’s top speed. The motor’s torque, measured between 40Nm and 120Nm, shows how well it climbs hills and accelerates. Riders can choose the perfect motor by understanding these specifications.
Types of eBike Motors Explained
Electric bikes come with three distinct motor configurations that offer unique characteristics and performance benefits.

Front Hub Motors
The front hub motor sits in the front wheel and needs less complex installation than other types. Its basic design makes maintenance a breeze since it doesn’t affect the bike’s drivetrain. Notwithstanding that, the motor’s extra weight on the front wheel can change the bike’s handling and reduce stability at high speeds. These motors work best for casual riders who stick to flat terrain or want a budget-friendly option.
Rear Hub Motors
Rear hub motors dominate 50-70% of the ebike motor market and create a more natural pushing feel while keeping the bike’s weight balanced. They grip better than front-mounted options, especially on hills and loose ground. The only drawback is that fixing flat tires becomes trickier with rear wheel removal. These motors keep handling predictable and stable, which makes them perfect for everything from daily commutes to hilly rides.

Mid-Drive Motors
The mid-drive motor’s position at the bike’s bottom bracket powers the crankset directly. This central location balances the bike’s weight better and sends more torque through existing gears. While these motors cost more and need complex installation, they shine on steep hills and use the bike’s gearing to boost performance on any terrain.
Hub Motor Variants: Geared vs Gearless
Hub motors also come in two variants – geared or gearless (direct drive) – each with its own mix of efficiency, weight, and maintenance needs.
Performance and Maintenance Considerations
Your choice of motor affects both your riding experience and how much you’ll spend on maintenance over time. Different motors create distinct sound levels. Direct drive hub motors run almost silently, and geared hubs make a soft whine when you speed up. Mid-drive motors create some mechanical noise because they work with the drivetrain, but new models like the TQ HPR50 run 1.8x quieter than other options.
Maintenance Factors by Motor Type
The motor’s location plays a big role in maintenance needs. Hub motors have fewer moving parts, which leads to 30-50% lower maintenance costs over time. Mid-drive systems, however, send power through the drivetrain and wear out parts faster. You’ll need to replace chains every 1,500-3,000 miles, while cassettes last 3,000-5,000 miles.
Battery Life and Riding Conditions
Your battery life changes based on the terrain and how you ride. Motors need more torque on hills, but flat ground works fine with lower power. Your weight and quick acceleration can drain the battery quickly.
Tips for Optimal Performance
To get the best performance:
- Keep your tires at the right pressure to roll easier
- Ride at a steady pace
- Choose the right gear, especially when you have mid-drives
Mid-drive motors work best on hills because they utilize the bike’s gearing system. Hub motors offer more consistent performance in different conditions and need much less maintenance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right eBike motor depends on your riding style and terrain. Front hub motors are simple and affordable, ideal for flat city rides. Rear hub motors deliver balanced weight and solid traction, making them great all-rounders. Mid-drive motors excel on hills and rough terrain thanks to their efficient use of the bike’s gearing system.Also you can read our comparison guide about Electric Bike Classes and Types also.
Maintenance and noise also matter, hub motors are quieter and need less upkeep, while mid-drives require more frequent drivetrain care. Battery performance varies with terrain, weight, and riding habits, so pick a setup that matches your needs.
Ready to experience smooth, powerful rides? Explore the latest electric bikes at Tesla Bike Sales and find the perfect motor for your journey today.
